Search results
Search for "laser-induced periodic surface structures (LIPSS)" in Full Text gives 3 result(s) in Beilstein Journal of Nanotechnology.
Laser-processed antiadhesive bionic combs for handling nanofibers inspired by nanostructures on the legs of cribellate spiders
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2022, 13, 1268–1283, doi:10.3762/bjnano.13.105

- sticking of an artificially nonwoven of nanofibers. According to the theoretical prediction, a technical analogon of the nanoripples was produced by ultrashort pulse laser processing on different technically relevant metal surfaces in the form of so-called laser-induced periodic surface structures (LIPSS
- randomly rough surfaces. The latter revealed that the adhesion of electrospun nanofiber nonwoven is significantly lowered on the nanostructured surfaces compared with the polished surfaces. Keywords: biomimetics; electrospinning; laser-induced periodic surface structures (LIPSS); nanofibers
- surface structure, in contrast to earlier published works where solids with plane surfaces were assumed [24][25][26][27][28]. This is an important difference, which has to be considered when modelling the interaction of nanofibers with, in this case, a sinusoidal surface. Laser-induced periodic surface
Femtosecond laser-assisted fabrication of chalcopyrite micro-concentrator photovoltaics
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 3025–3038, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.281
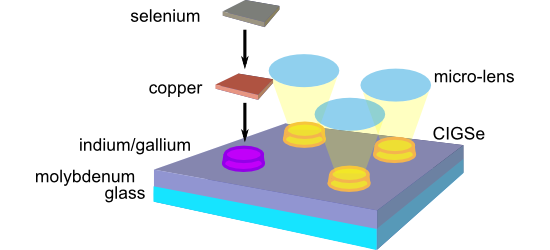
- -induced periodic surface structures (LIPSS [19]) and round melting features form on the glass surface (Figure 5b). The LIPSS with periods in the sub-micrometer range are generated via intra-pulse scattering and interference of the fs-laser radiation at the roughened glass surface, leading to the spatially
- of laser modifications on glass, which were recorded at tilting angles of 0 and 52° with respect to the surface normal, are depicted in Figure 5. Figure 5a shows a laser spot with slight surface roughening that increases towards the center. Using a somewhat higher laser fluence, pronounced laser
Biomimetic surface structures in steel fabricated with femtosecond laser pulses: influence of laser rescanning on morphology and wettability
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2802–2812, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.262

- surface topography needs to be mimicked, but often also a specific function of the structure. An alternative approach to laser direct writing of complex structures is the generation of laser-induced periodic surface structures (LIPSS), which is based on directed self-organization of the material and








































